

Let the enemy know - we fight for Ukraine and will not give them peace either on Earth or in the sky!

In today’s digital age, reliable and fast Internet access is essential for personal and professional purposes. Unfortunately, such civilization benefits are still not available to everyone. In rural or remote areas, in cities that are temporarily left without network access, broadband Internet access may not be available or prohibitively expensive. In such circumstances, satellite internet may be the only solution. This internet uses a satellite in geostationary orbit to provide network connectivity to users on the ground. In this article, we will talk about what satellite Internet is and delve into the principles of its operation, as well as its advantages and disadvantages.
Satellite Internet is a way of organizing access to the global network through satellite communication technologies. A satellite located in the geostationary orbit of the Earth is used to access the global network. Thanks to its engines, it always moves synchronously with the planet, and therefore, for an observer from its surface, the satellite is always stationary.

One satellite covers vast areas with a signal (theoretically, three satellites are enough to cover almost the entire habitable area of the planet). Address transmission of information (to each subscriber and not to a base station located on the surface of the Earth) became possible after the adoption of the DVB digital broadcasting standard.
Along with geostationary satellites, chains of low-flying satellites “communicate” with each other. Their signal can be received through a small antenna. Several satellites can be launched to distribute the supported frequency band evenly. The main drawback of the technology is that dozens and hundreds of low-flying satellites are needed to cover a large area.
Next, you will learn about what is satellite internet and what providers are.
Let’s trace the amazing story from the moment the launch of the satellite was a world event until the day when he started sending us cat videos to our Instagram feed.
The history of satellite Internet dates back to the 1960s when the US Department of Defense began to explore the possibility of using satellites to transmit data between remote locations. In 1962, the first satellite communication system called Telstar 1 was launched, which allowed television signals to be transmitted across the Atlantic Ocean.
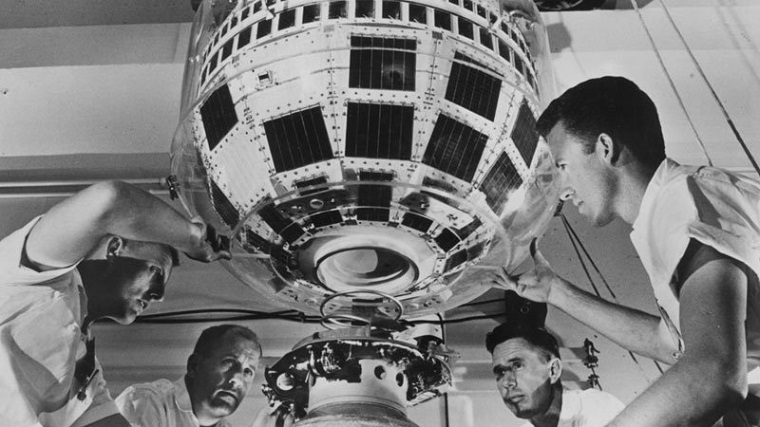

The first satellite to provide Internet services was launched in 1996, called the “Hughes Network System” or HNS-1. It was launched by Hughes Network Systems, a subsidiary of Hughes Electronics, which DirecTV later acquired. The HNS-1 satellite provided two-way high-speed Internet access to customers in North America using small satellite dishes installed in their homes or offices.
In the early 2000s, several companies, including Teledesic, Iridium, and Globalstar, launched satellites to provide global broadband Internet access. However, these ventures failed for various reasons, such as technical difficulties, high cost, and lack of demand.
In 2005, WildBlue Communications launched a satellite Internet service in the United States. The service provided high-speed Internet access in rural areas not served by traditional broadband providers. In 2008, ViaSat acquired WildBlue, which later launched an Exede-branded satellite internet service.
A major breakthrough in satellite internet came in 2015 when SpaceX announced plans to launch a network of thousands of low-earth orbit (LEO) satellites to provide high-speed, low-latency internet services to customers worldwide. The company began launching its Starlink satellites in 2019 and has nearly 2,000 satellites in orbit. Companies such as OneWeb, Amazon Project Kuiper, and Telesat also plan to launch their own LEO satellite constellations to provide global Internet access.

Satellite Internet has undergone significant changes in recent years. This technology has become more efficient, reliable, and affordable, allowing more people to access the internet, especially in rural or remote areas where traditional broadband services are unavailable. With the development of the LEO satellite constellations, satellite Internet is expected to become even more competitive with traditional broadband services regarding speed, latency, and availability.
Satellite Internet operates through two-way communication between a ground station or hub and a geostationary satellite that hovers 300 and 35,000 km above Earth’s surface. The hub communicates with the satellite, relaying the signal to a satellite dish or antenna installed at the client’s premises. The client’s modem then processes the signal, allowing it to access the internet.
There are two main types of satellite Internet: geostationary satellite Internet(GEO) and low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite Internet.
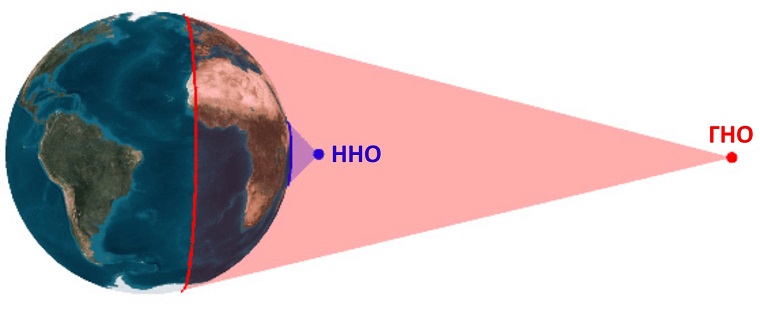
A traditional satellite Internet technology that has been in use for many years. The geostationary satellite remains in a fixed position relative to a distance of 35,000 kilometers from the Earth’s surface, allowing continuous coverage of a large area. This technology provides high bandwidth and is suitable for various applications such as video streaming, large file downloads, and online gaming. However, geostationary satellite Internet suffers from high latency, which can cause communication delays, especially in real-time applications.
A new technology that aims to overcome the latency problems of the geostationary satellite Internet. LEO satellites are located much closer to the Earth’s surface, typically at an altitude of 1200 km or less. This proximity reduces latency, resulting in faster communication between the client and the satellite. LEO satellite internet also provides more coverage than geostationary satellite internet because it uses a network of satellites that can move around and cover different areas of the Earth.
The LEO Satellite Internet Network is made up of a large number of small satellites that work together to provide communications. Starlink and Kuiper System use LEO. However, this technology is actively developed and improved.
The internet is used in almost all areas of human activity. But satellite Internet is indispensable in some of them:
Emergency response and recovery. In a natural disaster, traditional communications networks can be damaged, and satellite Internet can be quickly deployed to connect affected areas.
Maritime and aviation. Satellite Internet is being used by the maritime and aviation industries to communicate with ships, aircraft, and other vessels that travel to remote areas. This technology allows passengers and crew members to access the internet and stay connected.
Military and government agencies. Satellite communications are used by military and government agencies to provide secure and reliable communications in remote and hostile environments.
Enterprises. Satellite Internet is used by businesses that operate in remote areas or have branches in different locations. This technology allows them to link their offices and employees, share data and files, and access cloud services.
Rural and remote areas. As mentioned earlier, sometimes satellite internet is the only option for people living in remote, desert, and mountainous regions where cellular coverage or cable internet is simply not an option.

Several satellite internet providers in the market offer internet services to consumers. Here is an overview of the leading providers and their offerings:
Starlink is a satellite internet service offered by SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk. It currently provides internet service in select US, Canadian, and UK regions. Since the start of Russia’s full-scale military aggression in Ukraine, Elon Musk’s company has provided over 30,000 Starling terminals for Internet access for the Armed Forces of Ukraine and in areas left without electricity. The service offers download speeds from 50 Mbps to 150 Mbps and an average latency of 20-40 ms. Starlink provides a subscription-based service with a one-time payment of $599 for hardware and a monthly subscription fee of $110.
HughesNet is one of the oldest and most established satellite internet providers. It provides internet services to customers in the United States, offering download speeds from 25Mbps to 50Mbps and an average latency of 600ms. HughesNet offers several plans with different data caps and prices, ranging from 10GB to 50GB of data per month, ranging from $59.99 to $149.99 per month.

Viasat is another established satellite internet provider offering internet services to customers in the US. It provides download speeds from 12Mbps to 100Mbps and an average latency of 500-700ms. Viasat offers several plans with different data limits and prices, ranging from 12GB to 300GB of data per month, ranging from $50 to $200 per month.

OneWeb is a new entrant in the satellite internet market and is currently launching its satellite constellation. It aims to provide global Internet services with low latency and high speed. The company was on the verge of bankruptcy and canceled part of the launches from the Baikonur Cosmodrome as it refused to cooperate with the aggressor country and sponsor of terrorism. Nevertheless, OneWeb plans to start the first satellite launches in 2023. OneWeb project investors are well-known companies such as Airbus Group, Qualcomm Inc., The Coca-Cola Company, Virgin Group, etc.

Kuiper Systems is a satellite internet project launched by Amazon. It aims to provide high-speed Internet services to customers around the world. The project is still at an early stage. The service is not been fully launched yet. Amazon plans to launch 3236 satellites in the next decade.

Almost every large corporation either initiates its own satellite internet company or acts as one of the investors. There is a great chance that satellite communications will become another common technology available to everyone in the next 3-5 years.
Satellite Internet offers many advantages over traditional wired or wireless Internet services, but it also comes with some disadvantages. Here are some pros and cons of satellite internet:
Сovering. Satellites provide coverage in areas where traditional wired or wireless Internet service is unavailable or unreliable. This technology allows people living in remote or rural areas to access high-speed Internet services.
Speed. Providers offer high-speed Internet services with download speeds up to 100 Mbps and upload speeds up to 3 Mbps. This technology is ideal for video streaming and large file downloads.
Ease of deployment. Satellite Internet can be quickly deployed, making it ideal for emergency response and disaster recovery. This technology can provide connectivity to affected areas in the event of natural disasters, where traditional communication networks may be damaged.
Mobile connection. Such internet can provide direct connectivity to mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets, making it ideal for people who travel frequently or live in areas with limited connectivity.
Delay. Geostationary Satellite Internet suffers from high latency, which can cause communication delays, especially in real-time applications. The signal must travel a long distance between the satellite and the ground station, which can lead to delays. The new LEO technology is practically devoid of this drawback.
Price. Despite its growing popularity, satellite Internet is much more expensive than traditional wired or wireless Internet services. The cost of hardware, installation, and monthly subscription fees can be a barrier for many people.
Weather. Weather conditions such as rain, snow, and clouds can affect the connection quality. This may result in a slight decrease in Internet speed or loss of connection.
Data Limits. Satellite Internet providers often limit how much data users can upload or download to avoid network congestion. This can be a significant disadvantage for people who use the internet for streaming or other data-intensive applications.
Space debris. As you can see, satellite Internet still has some annoying shortcomings that can still be resolved in the future. Although the cost will decrease over time, this will give rise to a problem of little concern to the inhabitants. This is the problem of orbital pollution.
Old or defective satellites are much more difficult to dispose of than to launch, so the volume of space debris is constantly growing. Debris often flies uncontrollably and at high speeds, thus posing a significant threat to both research vehicles and new generations of satellites. Collision with such debris leads to the satellite’s destruction, eventually doubling the number of trash. Technologies for collecting space debris are already being developed, but since the threat does not yet seem serious, as well as a way to make money on it, such developments remain in the background.
You learned what is satellite internet, how it works, its pros and cons. You also learned that satellite Internet is still expensive and has some limitations. Despite the expensive connection and tariffs for many residents of villages remote from cities, this is the only means of communication. Like all new technologies, satellite Internet will gradually replace older, more familiar ones such as mobile or wired internet.